Table of Contents
- Key Points
- Understanding the Vaping Phenomenon
- The Chemical Impact of Vaping on Your Mouth
- Examining Teeth Before and After Vaping
- Vaping and Oral Cancer: A Growing Concern
- Additional Effects of Vaping on Oral Health
- Vaping Prevention and Treatment at ProGrin Dental
- Taking Action: Steps You Can Take Today
- Your Path to Better Oral Health
- References
Key Points
- While the first e-cigarette was invented well over 20 years ago, the global market for such products has only recently exploded in the past decade, with more than 58 million regular users worldwide today.1
- Most people know that vaping is bad for your heart, lungs, skin, and other parts of the body, but are uninformed about the impacts it can have on oral health.
- Understanding the relationship between vaping and dental health is vital for anyone who wants to stop vaping, and for encouraging individuals (especially young people) to never start.
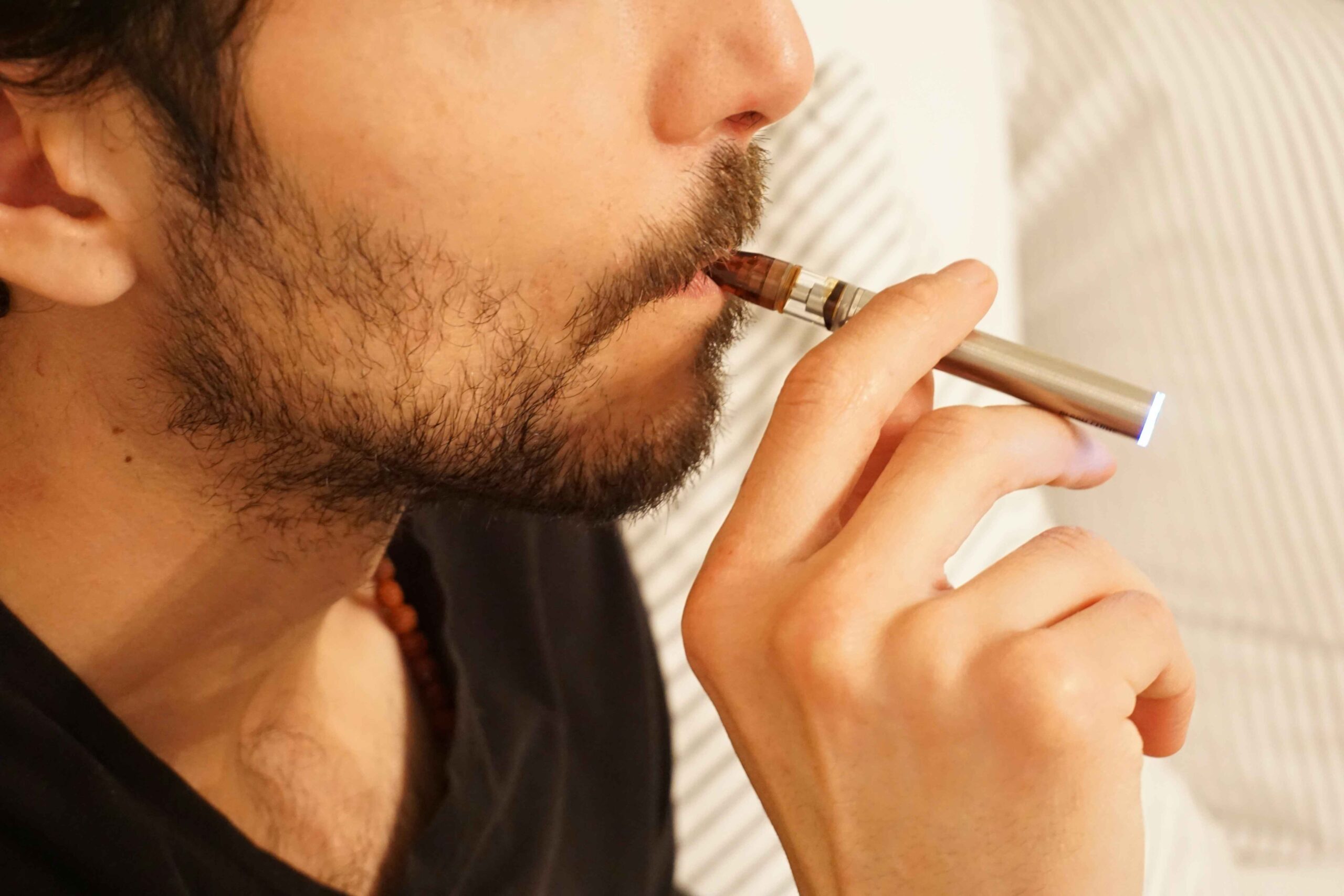
When electronic cigarettes, or “e-cigarettes,” first entered the scene, they were marketed as a safer alternative to traditional smoking. Research quickly revealed that that is not necessarily the case, or at least that the health distinctions are negligible. Use of both types of products can have serious consequences for respiratory, cardiovascular, and immune health.2
You can also add oral health to that list. A startling statistic from a recent study published by iScience reveals that more than 43 percent of young adults who vape show signs of gum disease, compared to just 28 percent of non-users.3 At ProGrin Dental, we are seeing firsthand how this “safer” alternative is creating serious oral health challenges that many patients do not realize until significant damage has already occurred.
The relationship between vaping and oral health is far more complex and concerning than many people realize. The effects of vaping on the mouth, gums, and teeth extend well beyond what meets the eye, impacting everything from your daily comfort to your long-term dental wellness. In this article, we explore this connection, including associated risks, and make recommendations that can help you stop vaping and optimize your oral health.
Understanding the Vaping Phenomenon
Electronic cigarettes and vaping devices work by heating a liquid solution that contains nicotine, propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, and various flavoring chemicals. When heated, this mixture creates an aerosol that users inhale directly into their mouths and lungs. This direct contact with oral tissues is where many of the dental problems begin.
The popularity of vaping has grown exponentially over the past decade. It is particularly attractive to teens and younger adults. According to a recent survey by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 2.3 million U.S. underage kids are current e-cigarette users.4
Some youth may believe that because vaping does not involve combustion like traditional cigarettes, it poses minimal risk to their teeth and gums. Unfortunately, this assumption has led to widespread dental issues that we are now recognizing and treating more frequently in our practice.
The Chemical Impact of Vaping on Your Mouth
The e-liquid used in vaping devices contains several chemicals that directly affect oral health. These harmful substances create a cascade of problems in your mouth:
- Propylene Glycol: Breaks down in the mouth to form acids that erode tooth enamel and irritate soft tissues, creating an environment where harmful bacteria can thrive.
- Vegetable Glycerin: Has a thick, sticky consistency that adheres to teeth and gums, trapping bacteria against tooth surfaces and interfering with saliva’s natural cleansing function.
- Flavoring Chemicals: Often contain compounds that cause inflammation in oral tissues and may contribute to cell damage, with some being particularly acidic and further compromising tooth enamel.
- Nicotine: Constricts blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient flow to oral tissues while also decreasing saliva production.5
The combination of these chemicals creates an environment where bacterial buildup accelerates, plaque formation increases, and the natural protective mechanisms of your mouth become compromised.
Examining Teeth Before and After Vaping
The transformation of teeth before and after vaping can be dramatic and concerning. Patients who have been vaping regularly often show visible changes in their oral health within months of beginning use. The progression typically follows a predictable pattern that becomes increasingly severe over time.
Visible Changes in Teeth:
- Discoloration: Initially, healthy teeth develop yellowish or brownish staining, particularly along the gum line, where vapors make the most contact.
- Enamel Erosion: Teeth lose their natural luster and may appear more translucent, especially at the edges.
- Increased Sensitivity: Weakened tooth structure leads to discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
- Structural Damage: Teeth become more susceptible to chips, cracks, and fractures due to compromised enamel.
Gum Changes:
- Color Changes: Healthy pink gums become red and inflamed.
- Swelling: Tissues appear puffy and enlarged.
- Bleeding: Gums bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
- Recession: Gum tissue pulls away from teeth, exposing sensitive root surfaces.
Perhaps most concerning is the accelerated rate of tooth decay that many vaping patients experience. Cavities may develop more quickly and in unusual locations, including areas that are typically less susceptible to decay in non-users. The combination of chemical exposure, bacterial growth, and reduced saliva production creates a perfect storm for dental deterioration.
Vaping and Oral Cancer: A Growing Concern
The relationship between vaping and oral cancer is an area of increasing research and concern within the dental and medical communities. While electronic cigarettes do not contain the tar and many carcinogens found in traditional tobacco products, they do contain potentially harmful chemicals that come into direct contact with oral tissues.
Carcinogenic Concerns:
- Chemical Exposure: Studies have identified formaldehyde and acetaldehyde, as well as other potentially carcinogenic compounds, in e-cigarette vapor.6
- DNA Damage: These substances can cause cellular damage that may contribute to cancerous changes over time.
- Direct Contact: Concentrated exposure occurs as chemicals are applied directly to the mouth, tongue, and throat.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent tissue irritation is a known risk factor for cancer development.
- Heat generation: Repeated exposure to high temperatures can damage oral tissues and may contribute to cellular changes that increase cancer risk. (Some users report burns or irritation from devices that malfunction or operate at excessive temperatures.7)
Additional Effects of Vaping on Oral Health
Beyond the more obvious impacts on teeth and gums, vaping affects oral health in numerous other ways that can significantly influence your quality of life:
Common Oral Health Issues from Vaping:
- Chronic Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva production leads to bacterial overgrowth and increased decay risk.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Chemical residues and bacterial buildup create stubborn halitosis.
- Impaired Wound Healing: Slower recovery after dental procedures due to reduced blood circulation.
- Taste and Smell Changes: Damaged taste buds and olfactory receptors diminish food enjoyment.
- Metallic Taste: Persistent unpleasant taste even when not actively vaping.
- Increased Infection Risk: Compromised immune response in oral tissues.
These secondary effects often compound the primary dental problems, creating a cycle of declining oral health that can be difficult to reverse without professional intervention and cessation of vaping.
Vaping Prevention and Treatment at ProGrin Dental
At ProGrin Dental, we believe in proactive care and patient education when it comes to vaping-related oral health issues. Our comprehensive approach addresses both immediate concerns and long-term prevention strategies:
- Enhanced Monitoring: More frequent dental cleanings and examinations to catch problems early.
- Targeted Therapies: Specialized treatments including fluoride applications, prescription mouth rinses, and periodontal therapy, as well as cosmetic treatments, if needed.
- Cessation Support: Resources and guidance for patients who want to quit vaping.
- Protective Measures: Custom solutions to minimize ongoing damage for current users.
- Comprehensive Screening: Regular oral cancer screenings and advanced diagnostic techniques.
For patients showing early signs of enamel erosion or gum disease related to vaping, we may recommend additional protective measures to help preserve remaining tooth structure and promote healing of affected tissues. Our team works closely with each patient to develop personalized treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals.
Taking Action: Steps You Can Take Today
If you are currently vaping, there are immediate steps you can take to minimize further damage to your oral health:
- Increase Oral Hygiene: Brush at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to combat dry mouth and help flush away harmful chemicals.
- Use Fluoride Rinse: Consider an alcohol-free mouth rinse to help strengthen enamel.
- Schedule Regular Checkups: Visit ProGrin Dental more frequently for monitoring and prevention.
- Consider Cessation: Most importantly, explore options for quitting vaping to prevent further damage.
Your Path to Better Oral Health
The effects of vaping on oral health are far-reaching and often more severe than users anticipate. From enamel erosion and gum disease to potential cancer risks, the impact on dental wellness can be significant and long-lasting. While vaping may seem like a safer alternative to traditional smoking, the evidence clearly shows that it poses serious risks to oral health that should not be ignored.
If you are currently vaping or considering it as an alternative to smoking, we encourage you to discuss the oral health implications with our team at ProGrin Dental. Early intervention and proper monitoring can help minimize damage and preserve your dental health.
For those ready to quit, we are here to support your journey toward better oral and overall health, with a supportive, non-judgmental approach. Schedule your consultation today to learn more about protecting your smile from the hidden dangers of vaping.
References
- Tomasz Jerzyński, Gerry V. Stimson, Harry Shapiro, and Grzegorz Król, “Estimation of the global number of e-cigarette users in 2020,” Harm Reduction Journal, October 2021, https://harmreductionjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12954-021-00556-7.
- Patrice Marques, Laura Piqueras, and Maria-Jesus Sanz, “An updated overview of e-cigarette impact on human health,” Respiratory Research, May 2021, https://respiratory-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12931-021-01737-5.
- Smruti Pushalkar, Bidisha Paul, Qianhao Li, et al., “Electronic Cigarette Aerosol Modulates the Oral Microbiome and Increases Risk of Infection,” iScience, March 2020, “https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(20)30068-7.
- Eunice Park-Lee, PhD; Ahmed Jamal, MBBS; Hannah Cowan, MPH; et al., “Notes from the Field: E-Cigarette and Nicotine Pouch Use Among Middle and High School Students — United States, 2024,” Mobility and Mortality Weekly Report, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, September 2024, https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/73/wr/mm7335a3.htm.
- Sangeeta Gajendra, Scott McIntosh, and Sucharu Ghosh, “Effects of tobacco product use on oral health and the role of oral healthcare providers in cessation: A narrative review,” Tobacco Induced Diseases, January 2023, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9875717/.
- Leon Kosmider, Sharon Cox, Marzena Zaciera, et al., “Daily exposure to formaldehyde and acetaldehyde and potential health risk associated with use of high and low nicotine e-liquid concentrations,” Scientific Reports, Nature.com, April 2020, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-63292-1.
- Samantha Brophy, Jackie Combs, and Julia Hutchison, “Thermal Pharyngeal Injury Resulting From Vaping: A Case Report,” Cureus, June 2024, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11226206/.
Dr. Greg Ayers has over 35 years of experience running his own dental practice. He is the CEO and clinical director of ProGrin Dental and Cosmetics, which he and his son founded in 2012. Dr. Ayers is a graduate of the Medical University of South Carolina’s College of Dental Medicine, then furthered his dental education at the Pankey Institute for Advanced Dental Learning. Dr. Ayers is also a graduate of the acclaimed Nash Institute for Dental Learning, and he currently serves as a teaching mentor at the Institute, working with doctors and healthcare professionals from around the world. Dr. Ayers has also authored two books: “The Service Prescription – Healthcare the Way it Was Meant to Be,” and a motivational book entitled “SPARK, Igniting Your Dreams.”